Job Shortages
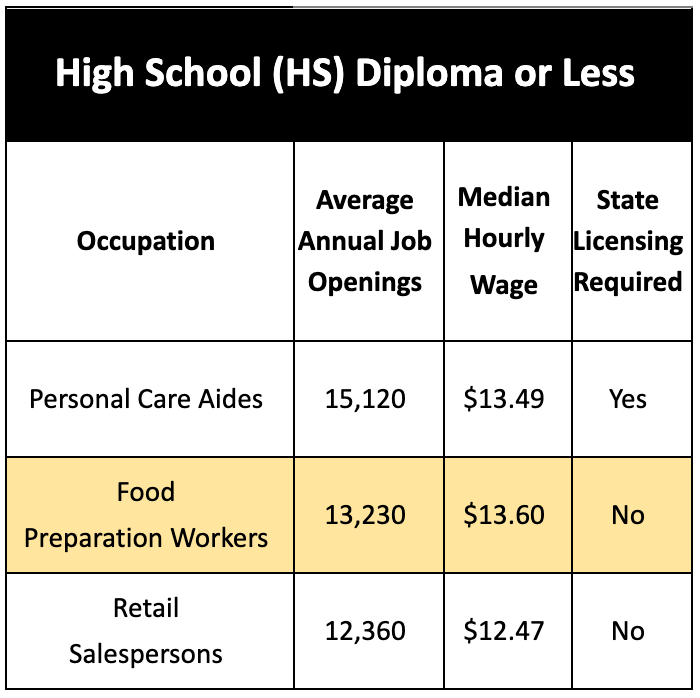
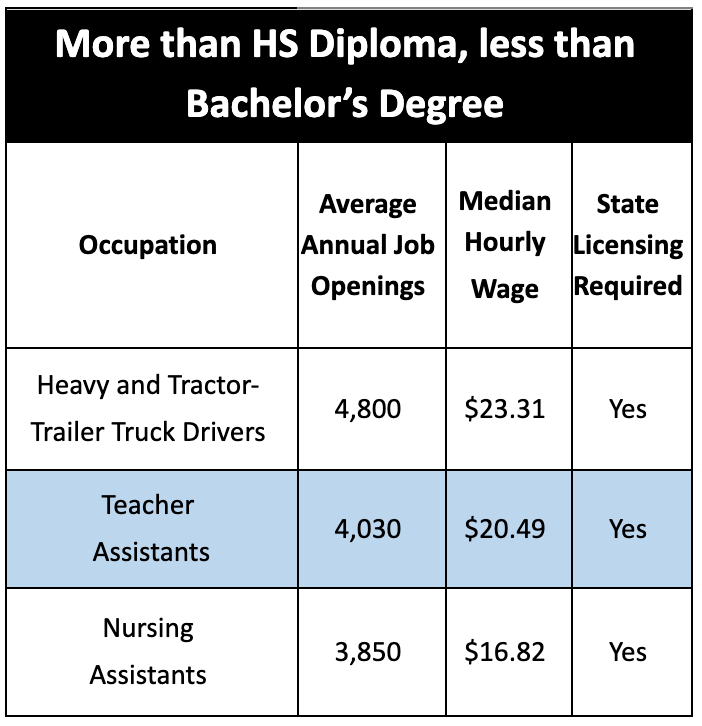
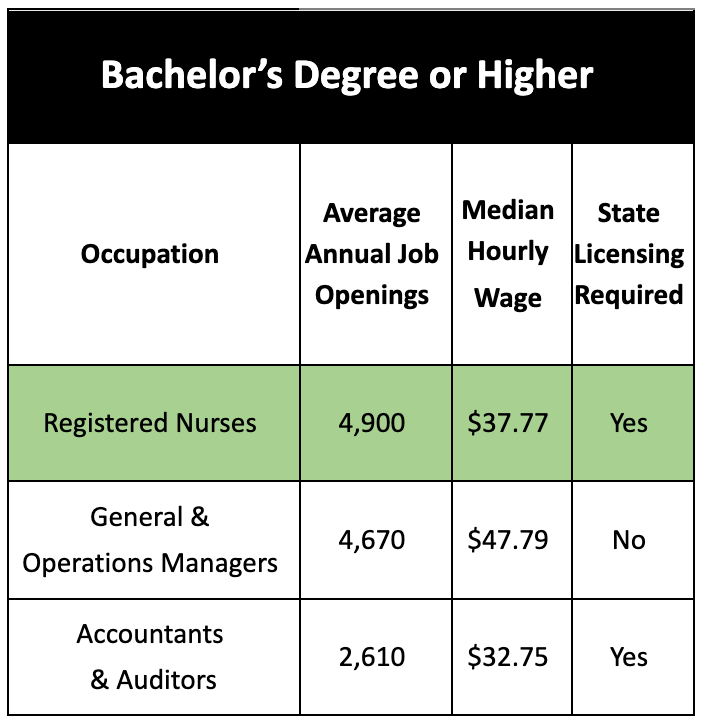
The tables below show the top three occupations that are projected from 2018-2028 of Minnesota employers based on the level of education they require. There is a state minimum wage of $8.15 for businesses with less than $500k in annual sales and $10.00 for those above $500k annual sales in Minnesota. The one highlighted occupation under each of the three education levels has been selected to expand on in terms of potential career advancement.
Potential Career Advancement
1) Food Preparation Worker to Certified Food Manager
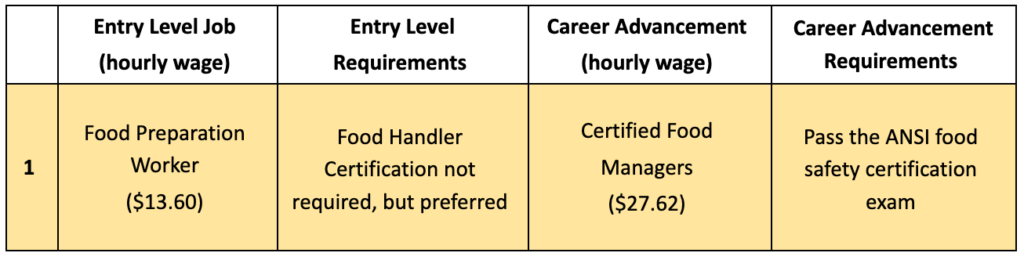
Food Preparation Worker Job Description:
- Perform a variety of food preparation duties other than cooking
Entry Level Requirements:
- Food Handler Certification – not required by Minnesota state law, but employers may prefer it
- Obtain Food Handler Certification online here ($7, 2 hours); click here to take exam in Español, 普通话, 한국어, Việt, American Sign Language, Tagalog, Serbo-Croatian
Certified Food Manager Job Description:
- Responsible for food safety to protect the public from foodborne illness
Career Advancement Requirements:
- Pass the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) certification exam ($55)
- Online courses are not required, but provide knowledge for the ANSI exam
2) Teacher Assistant to Elementary School Teacher
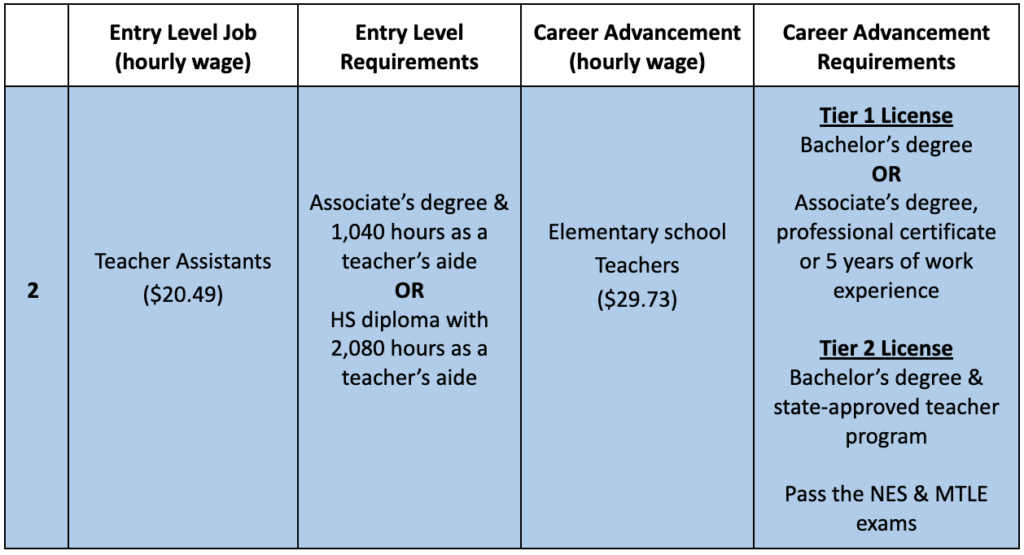
Teacher Assistant Job Description:
- Assist in the teaching of academic and social skills to students at any and all school levels
Entry Level Requirements:
- Associate’s degree & 1,040 hours as a teacher’s aide OR High School Diploma and 2,080 hours as a teacher’s aide
- Other accepted combinations of education and experience required are here
Elementary School Teacher Job Description:
- Teach academic and social skills to students at the elementary school level
Career Advancement Requirements:
- Minnesota has a tiered licensure system for teaching with different requirements for each tier
- Tier 1 license has least strict entry requirements – Bachelor’s degree OR either an associate’s degree, professional certification or 5 years of relevant work experience
- Tier 2 typically requires completion of a state-approved teacher preparation program
- Tier 3 requires passing scores on content and pedagogy exams
- Minnesota NES Essential Academic Skills (EAS) exam – test preparation materials here
- Minnesota Teacher Licensure Examinations (MTLE) for Pedagogy: Elementary (Grades K-6) exam & the MTLE Elementary Education (Grades K-6) exam – test prep materials here
3) Registered Nurse to Nurse Practitioner
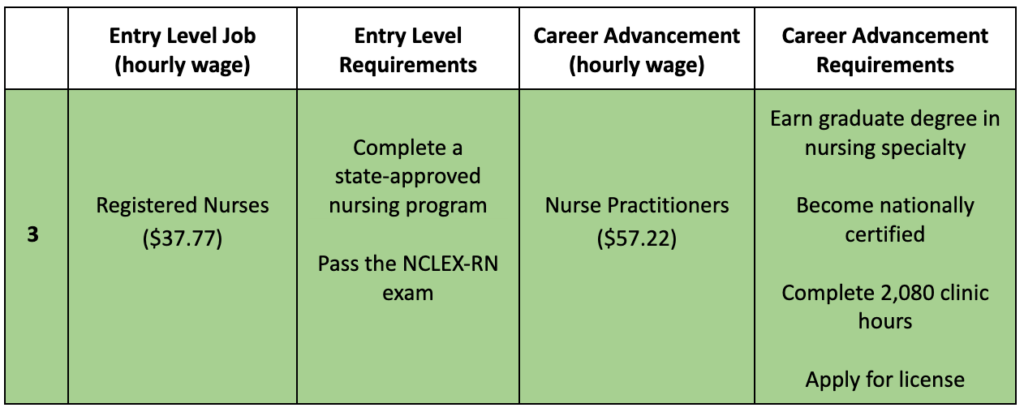
Registered Nurse Job Description:
- Assess patient health problems and needs, develop and administer nursing care
Entry Level Requirements:
- Complete a state-approved nursing program
- Pass the National Council Licensure Examination-Registered Nurse (NCLEX-RN) exam ($200)
Nurse Practitioner Job Description:
- Diagnose and treat patients independently or as part of a healthcare team
Career Advancement Requirements:
- Earn a graduate degree in a chosen nursing specialization
- Become nationally certified by an accredited agency
- Apply for licensure while completing 2,080 clinic hours in a healthcare setting
Immigration in Minnesota
The following are facts about the immigrant community in Minnesota:
- Immigrants comprise 9% of the state population and 11% of the Minnesota labor force
- Top industries of immigrant employment:
- Health Care and Social Assistance, 65,425 workers
- Manufacturing, 63,707 workers
- Retail Trade, 35,742 workers
- Educational Services, 29,921 workers
- Accommodation and Food Services, 29,737 workers
- 20,219 immigrant business owners account for 7% of all self-employed Minnesota residents
- 53% of immigrants in Minnesota are naturalized and another 20% are undocumented
- Top foreign-born countries of origin:
- Mexico, 12%
- Somalia, 8%
- India, 6%
- Laos, 5%
- Ethiopia, 5%
- 7% of native-born Minnesotans are children of an immigrant
- Educational attainment of foreign born adults in Minnesota:
- High School diploma or less – 44%
- More than HS diploma, less than Bachelor’s degree – 22%
- Bachelor’s degree or higher – 34%
- Share of Brain Waste* – 23%
* Share of immigrant professionals, who are unemployed, employed at poverty-level wages in High School diploma or less jobs, or significantly underemployed in more than HS diploma, less than Bachelor’s degree jobs
Sources
Jobs
Projections Managing Partnership (PMP), Projections Central – State Occupational Projections, “Long Term Occupational Projection (2018-2028)”; http://www.projectionscentral.com/Projections/LongTerm
Bureau of Labor Statistics, May 2019 State Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates; https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oessrcst.htm
Bureau of Labor Statistics, Employment Projections, “Education and training assignments by detailed occupation,” 2019; https://www.bls.gov/emp/tables/education-and-training-by-occupation.htm
National Council of State Legislatures, “State Minimum Wages”, December 2020; http://www.ncsl.org/research/labor-and-employment/state-minimum-wage-chart.aspx#Table
Bureau of Labor Statistics, Economic News Release, “Employees on Nonfarm Payrolls by State, Seasonally adjusted”, November 2020; https://www.bls.gov/news.release/laus.t03.htm
Potential Career Advancement
National Conference of State Legislatures, “The National Occupational Licensing Database”, March 2020: https://www.ncsl.org/research/labor-and-employment/occupational-licensing-statute-database.aspx
Immigration
American Immigration Council, State by State Fact Sheet, August 2020; https://www.americanimmigrationcouncil.org/topics/state-by-state